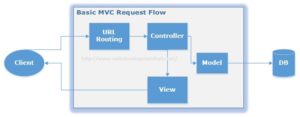
ASP.NET MVC is a framework that facilitates building web applications based on MVC (Model-View-Controller) design pattern. Request coming from client reaches the Controllerthrough URL Rewriting Module. Controller decides which model to use in order to fulfill the request. Further passing the Model data to View which then transforms the Model data and renders response to client as shown in following basic level request flow diagram.
In this ASP.NET MVC Tutorial, we will discuss and implement different options to pass data from ASP.NET MVC Controller to View. Following are the available options to pass data from a Controller to View in ASP.NET MVC:
- ViewBag
- ViewData
- TempData
If we want to maintain state between a Controller and corresponding View- ViewData andViewBag are the available options but both of these options are limited to a single server call (meaning it’s value will be null if a redirect occurs). But if we need to maintain state from one Controller to another (redirect case), then TempData is the other available option.
It’s common that initially it might be a bit difficult for a ASP.NET WebForms developer to digest above flow and need for options to pass data from Controller to View. Because in WebForms approach, Controller and View are tightly coupled to each other.
ViewBag Example
As we discussed earlier that ViewBag and ViewData serves the same purpose but ViewBag is basically a dynamic property (a new C# 4.0 feature) having advantage that it doesn’t have typecasting and null checks.
So, In order to pass data from Controller to View using ViewBag, we will modify our EmployeeController code as follows:
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
// GET: /Employee/
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.EmployeeName = “Muhammad Hamza”;
ViewBag.Company = “Web Development Company”;
ViewBag.Address = “Dubai, United Arab Emirates”;
{
// GET: /Employee/
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.EmployeeName = “Muhammad Hamza”;
ViewBag.Company = “Web Development Company”;
ViewBag.Address = “Dubai, United Arab Emirates”;
return View();
}
}
}
}
And to get Employee details passed from Controller using ViewBag, View code will be as follows:
<body>
<div>
<h1>Employee (ViewBag Data Example)</h1>
<div>
<b>Employee Name:</b> @ViewBag.EmployeeName<br />
<b>Company Name:</b> @ViewBag.Company<br />
<b>Address:</b> @ViewBag.Address<br />
</div>
</div>
</body>
<div>
<h1>Employee (ViewBag Data Example)</h1>
<div>
<b>Employee Name:</b> @ViewBag.EmployeeName<br />
<b>Company Name:</b> @ViewBag.Company<br />
<b>Address:</b> @ViewBag.Address<br />
</div>
</div>
</body>
In order to see the above changes in action run the solution, we will find the following output.

ViewData Example
As compared to ViewBag, ViewData is a dictionary object which requires typecasting as well as null checks. Same above implementation using ViewData can be achieved as follows:
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
// GET: /Employee/
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData[“EmployeeName”] = “Muhammad Hamza”;
ViewData[“Company”] = “Web Development Company”;
ViewData[“Address”] = “Dubai, United Arab Emirates”;
{
// GET: /Employee/
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData[“EmployeeName”] = “Muhammad Hamza”;
ViewData[“Company”] = “Web Development Company”;
ViewData[“Address”] = “Dubai, United Arab Emirates”;
return View();
}
}
}
}
And to get Employee details passed from Controller using ViewBag, View code will be as follows:
<body>
<div>
<h1>Employee (ViewBag Data Example)</h1>
<div>
<b>Employee Name:</b> @ViewData[“EmployeeName”]<br />
<b>Company Name:</b> @ViewData[“Company”]<br />
<b>Address:</b> @ViewData[“Address”]<br />
</div>
</div>
</body>
<div>
<h1>Employee (ViewBag Data Example)</h1>
<div>
<b>Employee Name:</b> @ViewData[“EmployeeName”]<br />
<b>Company Name:</b> @ViewData[“Company”]<br />
<b>Address:</b> @ViewData[“Address”]<br />
</div>
</div>
</body>
Run the application to view the following output.

No comments:
Post a Comment